home > Pablication
2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010
2009 2008 1998–2007
“Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence of Dibenzophenazine-Cored Phenazaborines in Solid State: Anion Modulation of Photophysics"
Jaijanarthanan Lingagouder, Nae Aota, Riku Nakagawa, Beata Luszczynska, Satoshi Minakata, Leonardo Evaristo de Sousa, Piotr de Silva*, Przemyslaw Data*, and Youhei Takeda*
J. Phys. Chem. C 2024, 39, 16805–16812. DOI:10.1021/acs.jpcc.4c05319
*Invited as a part of a Special Issue on "TADF-Active Systems: Mechanism, Applications, and Future Directions"!
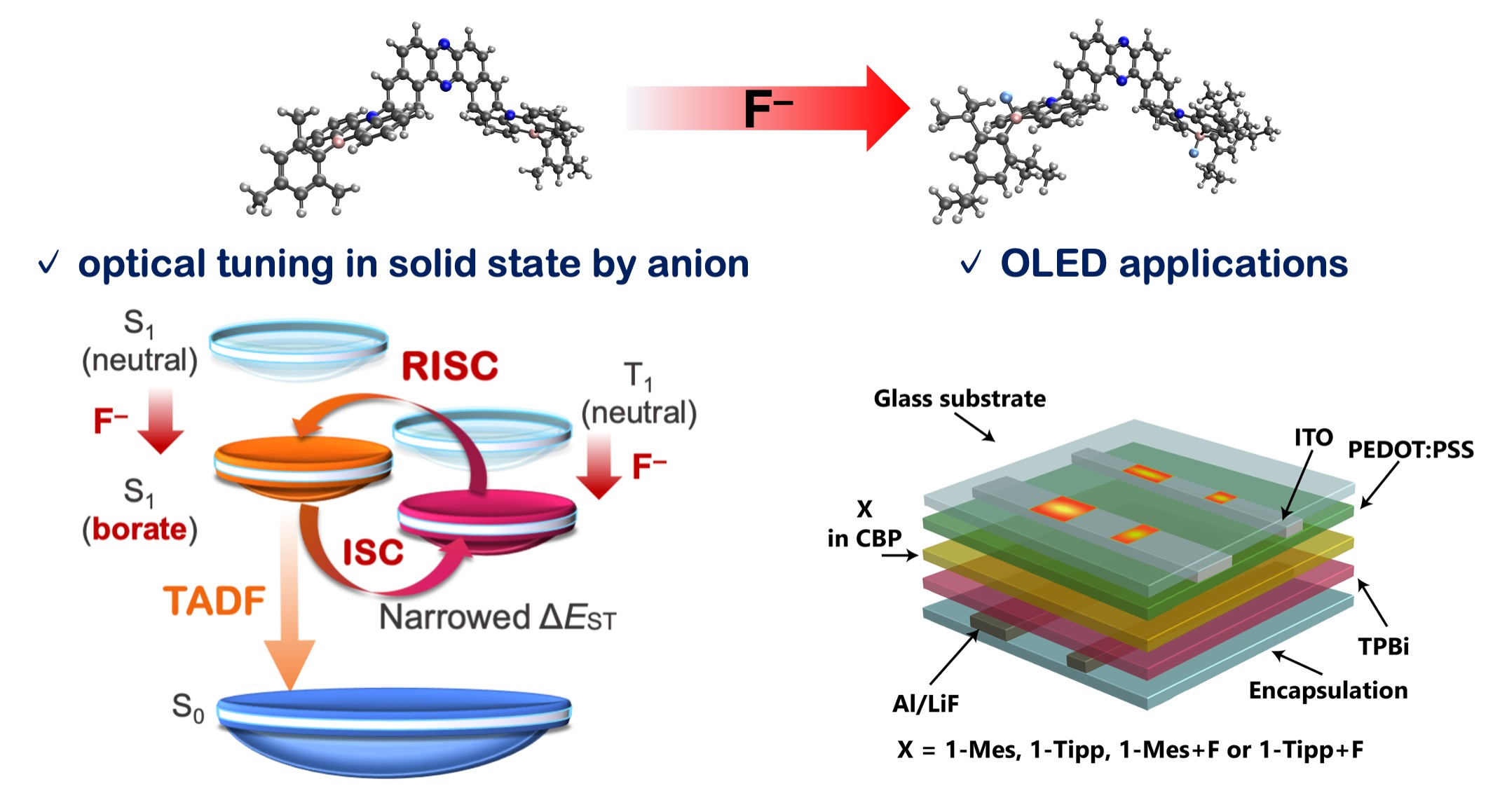
Abstract: The relentless pursuit of high-performance organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) necessitates the exploration of novel materials with efficient light emission. Herein, we report donor–acceptor–donor (D–A–D) compounds, incorporating dibenzo[a,j]phenazine (DBPHZ) as the acceptor (A) and phenazaborine (PAzB) derivatives as the donors (D), embedded in various hosts, and investigate their impact on emission mechanisms. This study examines the effect of strategic fluorination of the trivalent boron center on the performance of the D–A–D compounds as solid-state emitters. The incorporation of fluoride into the D–A–D compounds within the matrix films resulted in a red shift in the photoluminescence (PL) emission. Additionally, we evaluated the influence of fluoride addition on the delayed emission characteristics of the D–A–D-containing films. This solid-state modulation technique demonstrated a potential applicability to OLEDs. Quantum chemical calculations elucidated how fluoride incorporation alters the photophysical properties of the compounds by modifying the electronic characteristics of the excited states.
“Anion-Responsive Colorimetric and Fluorometric Red-Shift in Triarylborane Derivatives: Dual Role of Phenazaborine as Lewis Acid and Electron Donor"
Nae Aota, Riku Nakagawa, Leonardo Evaristo de Sousa, Norimitsu Tohnai, Satoshi Minakata, Piotr de Silva*, and Youhei Takeda*
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202405158/1–10. DOI:10.1002/anie.202405158
*Open-access article"!
*Selected as a "HOT Paper"!
*Press Release
*Highlighted in Resou, EurekAlert!, Optronics, Asia Research News, Phys.Org., ScienceDaily!
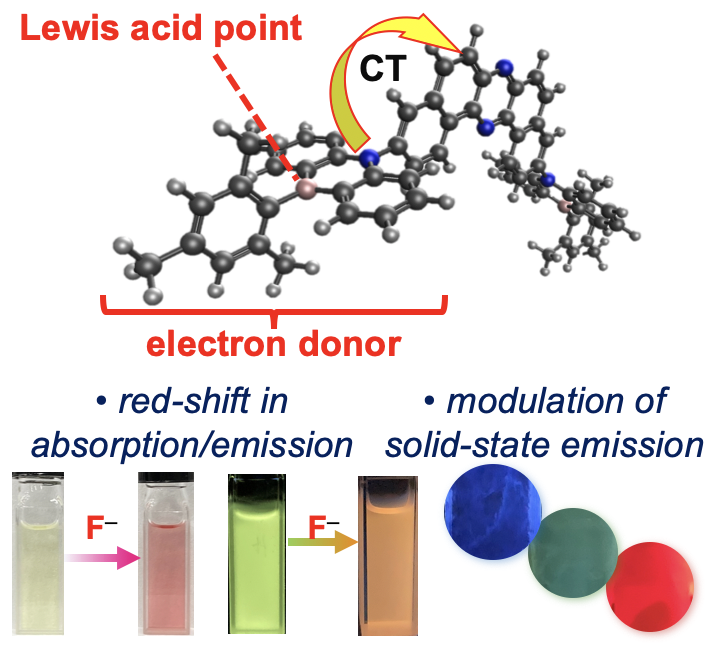
Abstract: A strategy of modulating photophysical properties by balancing the contradictory role of phenazaborine as a Lewis acid and an electron donor has been used to synthesize anion-responsive triarylborane compounds that displayed significant red-shift in their absorption and photoluminescence spectra in solution. This approach has also been successfully applied to modulate the emission color in polymer films.
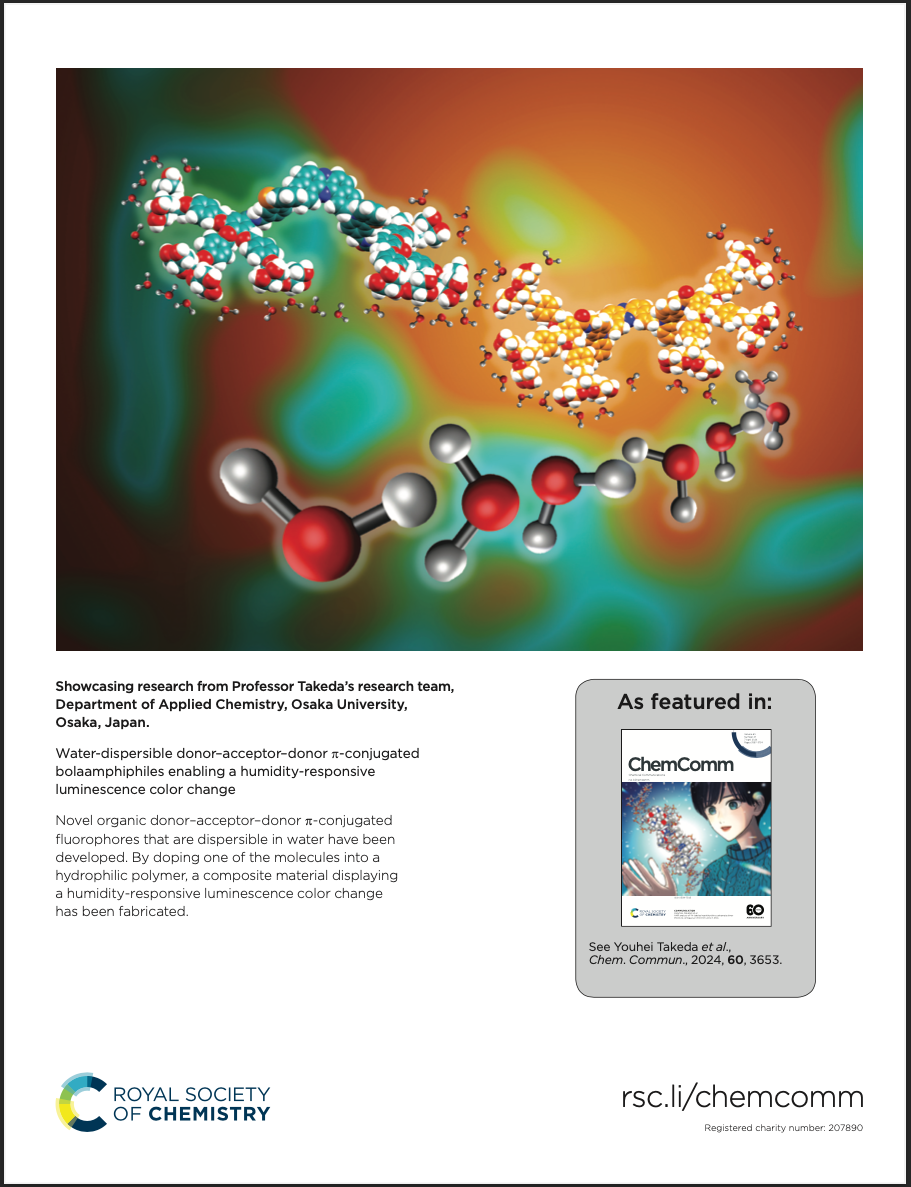
“Water-Dispersible Donor–Acceptor–Donor π-Conjugated Bolaamphiphiles Enabling a Humidity-Responsive Luminescence Color Change"
Tomoya Enjou, Shimpei Goto, Qiming Liu, Fumitaka Ishiwari, Akinori Saeki, Taro Uematsu, Yuka Ikemoto, Sora Watanabe, Go Matsuba, Kouichiro Ishibashi, Go Watanabe, Satoshi Minakata, Yoshimitsu Sagara, and Youhei Takeda*
Chem. Commun. 2024, 60, 3653–3656. DOI:10.1039/D3CC05749F
*Open-access article"!
*Invited as a part of a Themed Collection on "CC 60th Anniversary Authors Collection"!
*Selected as the "ChemComm Most Popular 2024 Articles"!
*Highlighted in the "Interview of Chemical Communications Blog"!
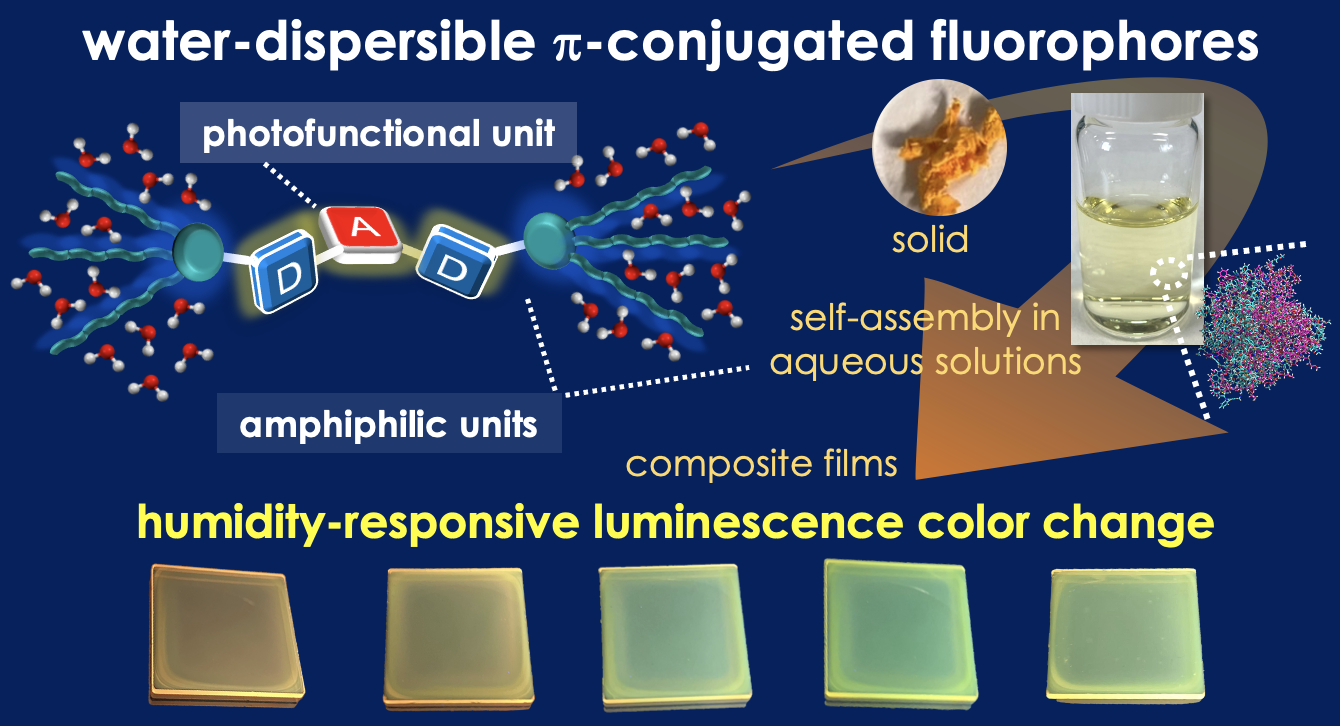
Abstract: Novel water-dispersible donor–acceptor–donor π-conjugated bolaamphiphiles, having dibenzophenazine as the acceptor and heteroatom-bridged amphiphilic diarylamines as the donors, have been developed. The materials displayed a distinct photoluminescence color change in response to humidity in a poly(vinylalcohol) matrix.
“Amino-λ3-iodane-Enabled Electrophilic Amination of Arylboronic Acid Derivatives"
Kensuke Kiyokawa*, Kazuki Kawanaka, and Satoshi Minakata*
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202319048/1–6. DOI:10.1002/anie.202319048
*Open-access article"!
*Selected as a HOT Paper"!

Abstract: In this report, we describe the use of amino-λ3-iodanes in the electrophilic amination of arylboronic acids and boronates. Iodine(III) reagents with transferable amino groups, including one with an NH2 group, were synthesized and used in the amination, allowing the synthesis of a wide range of primary and secondary (hetero)arylamines. Mechanistic studies by DFT calculations indicate that the reaction proceeds through an electrophilic amination process from a tetravalent borate complex with a B−N dative bond.
“Photoexcitation of (Diarylmethylene)amino Benziodoxolones for Alkylamination of Styrene Derivatives with Carboxylic Acids"
Daichi Okumatsu, Kensuke Kiyokawa,* Linh Tran Bao Nguyen, Manabu Abe*, and Satoshi Minakata*
Chem. Sci. 2024, 15, 1069-1076. DOI:10.1039/D3SC06090Jz
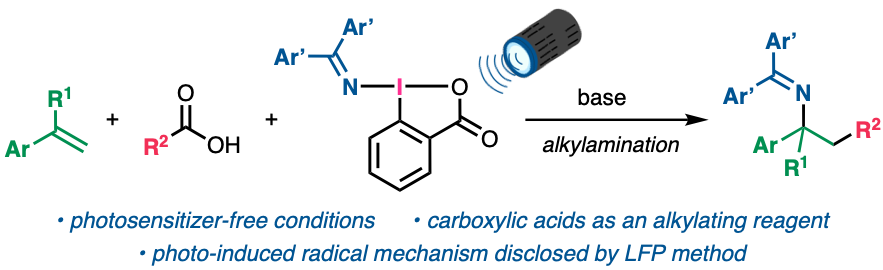
Abstract: The alkylamination of alkenes using pristine carboxylic acids was achieved by the photoexcitation of (diarylmethylene)amino benziodoxolones (DABXs), which serve as both an oxidant and an aminating reagent (an iminyl radical precursor). The developed method is a simple photochemical reaction without the need for external photosensitizers and shows a broad substrate scope for aliphatic carboxylic acids leading to the formation of primary, secondary, and tertiary alkyl radicals, thus enabling the facile synthesis of various structurally complex amines. Mechanistic investigations including transient absorption spectroscopy measurements using a laser flash photolysis (LFP) method disclosed the unique photochemical reactivity of DABXs, which undergoes homolysis of their I–N bonds to give an iminyl radical and ortho-iodobenzoyloxy radical, the latter of which participates in the single-electron oxidation of carboxylates.