2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010
2009 2008 1998–2007
“Bromamine-T"
Rajenahally V. Jagadeesh, Puttaswarmy, and Satoshi Minakata
First Update In Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis 2026. DOI:10.1002/047084289X.rn01612.pub2
Abstract: In this article, recent examples of the use of Bromamin-T in organic synthetic reactions are presented.
“Oxidative α-Amination and Aziridination of Cyclic β-Ketoesters Using Aminobenziodoxolones"
Kazuki Kawanaka, Kotaro Muraoka, Kensuke Kiyokawa*, and Satoshi Minakata*
Org. Lett. 2025, 27, 13607–13613. DOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.5c04501
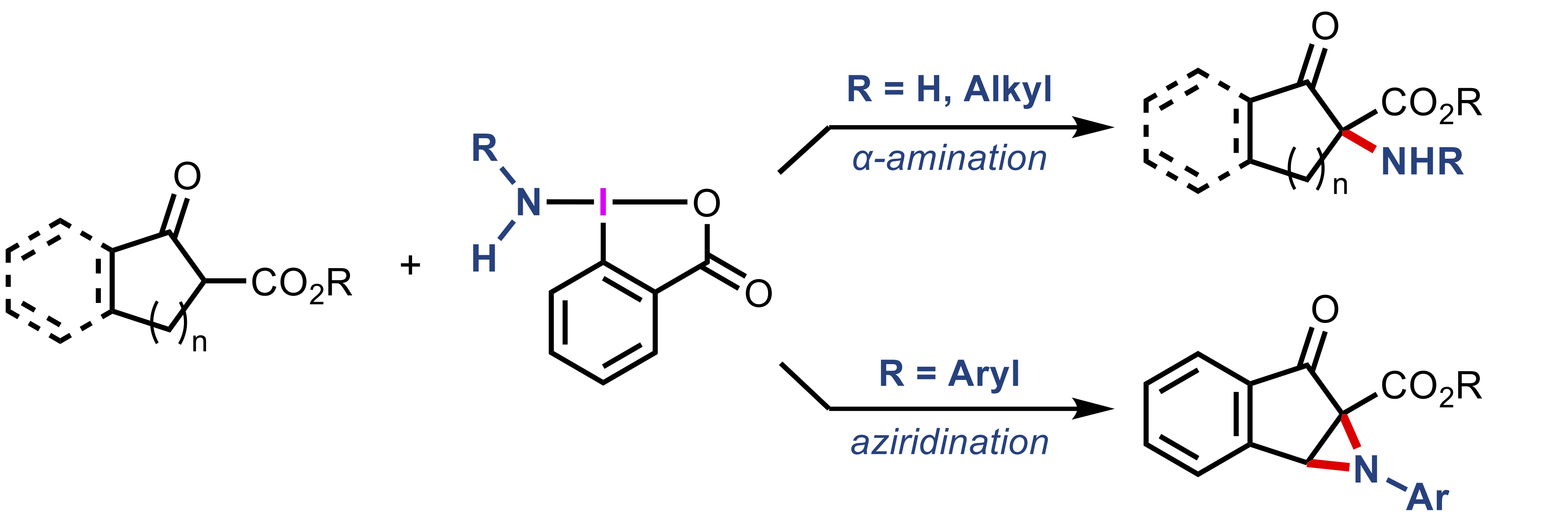
Abstract: The oxidative amination of β-ketoesters with hypervalent iodine reagents bearing transferable amino groups (aminobenziodoxolones) is described. NH2-substituted and alkylamine-derived aminobenziodoxolones enable electrophilic α-amination, whereas the use of arylamine-derived reagents promotes aziridination to afford fused aziridines. The developed methods expand the scope of accessible α-amino-β-ketoester scaffolds, which represent unique and valuable synthetic intermediates for the construction of nitrogen-containing compounds.
“Highly soluble cyclic dibenzophenazine heterodimer enabled by a tetra-functionalized building block"
Naohiro Hamba, Fumiya Ogura, Marc K. Etherington, Satoshi Minakata*, and Youhei Takeda*
Chem. Lett. 2025, 54, upaf216/1–5. DOI:10.1093/chemle/upaf216
*Open-access article"!
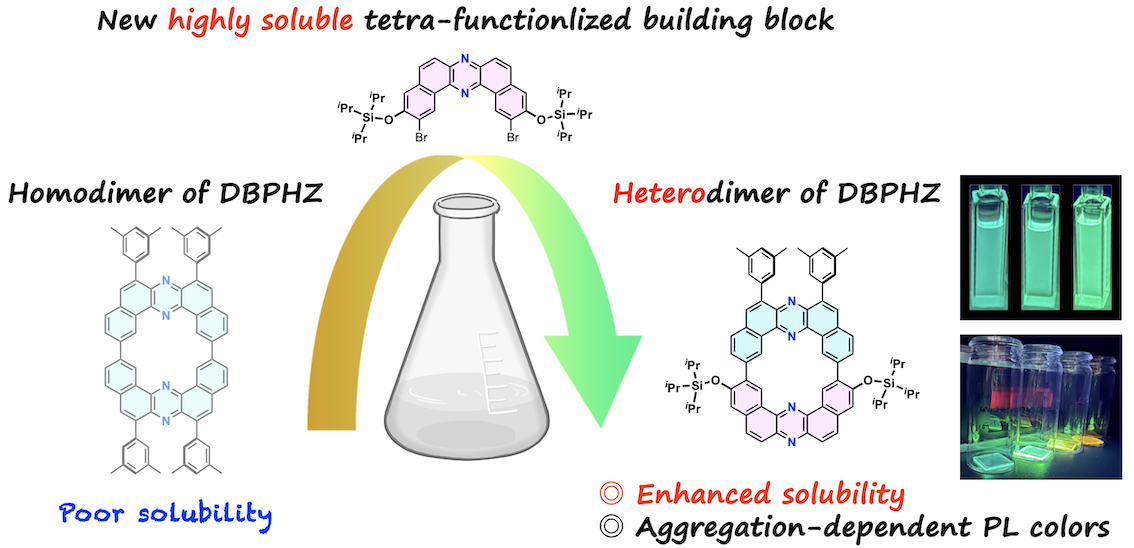
Abstract: A cyclic heterodimer of dibenzo[a,j]phenazine (DBPHZ) has been synthesized using a novel tetra-functionalized DBPHZ building block bearing bulky siloxy and dibromo substituents. Siloxy groups markedly enhanced the solubility of both the resulting intermediates and the macrocycle, enabling facile purification and systematic photophysical studies. The heterodimer exhibits locally excited fluorescence with minimal solvent dependence in solutions and pronounced aggregation-induced red-shifted emission in the films. This study demonstrates a molecular design strategy to enhance solubility and processability of nitrogen-embedded π-conjugated macrocycles.
“Aggregation-Induced Energy Transfer Within a Donor–Acceptor–Donor Compound Featuring Hydrophobic Mesogenic Self-Assembling Units"
Ryota Usami, Koichiro Ishibashi, Nae Aota, Go Watanabe*, Yoshiya Omori, Tsuneaki Sakurai, Masaki Shimizu, Satoshi Minakata, and Youhei Takeda*
Chem. Asian J. Early View, e70426/1–8. DOI:10.1002/asia.70426
*Open-access article"!
*Invited as a part of a Honorary Collection on "In Memory of Professor Masahiko Iyoda"!
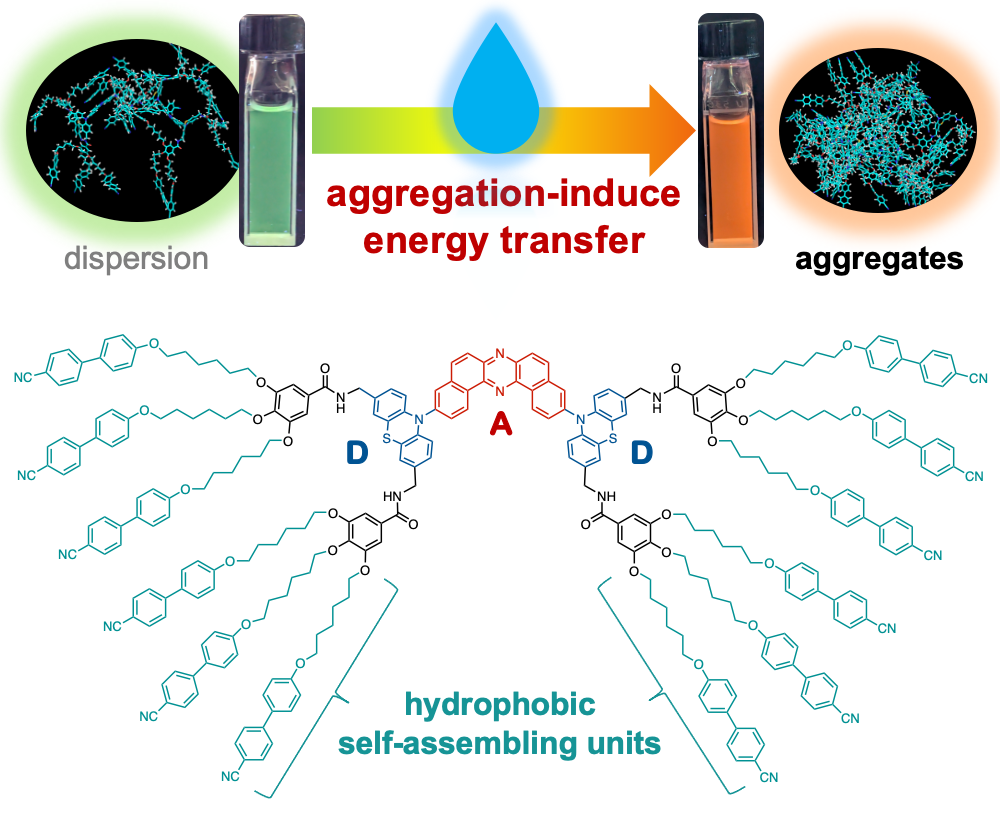
Abstract: In this study, we report the design and synthesis of a novel donor–acceptor–donor-type organic emitter incorporating hydrophobic starburst mesogenic units. We have demonstrated that, in aqueous environments, this compound undergoes aggregation that induces efficient energy transfer within the molecules, resulting in tunable shifts in emission color. Molecular dynamics simulations corroborate the proposed mechanism by revealing the intramolecular assembly behavior. These findings provide valuable insights for the rational design of functional nano-aggregates targeted for applications in sensing and photonic materials.
“Synthesis and Photophysical Properties of Cyclic Homodimer of U‑Shaped Dibenzophenazinylene"
Naohiro Namba, Satoshi Minakata*, and Youhei Takeda*
Org. Lett. 2025, 27, 11480–11484. DOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.5c03358
*Invited as a part of a Special Issue on "π-Conjugated Molecules & Materials"!
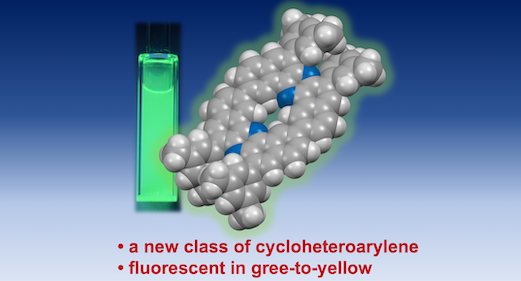
Abstract: A new class of cyclic π-extended heteroarylene oligomer─cyclic homodimer of U-shaped dibenzophenazinylene─has been successfully synthesized and characterized. NMR spectroscopy and DFT calculations implicated the unique topologies of the macrocycle. The cyclic dimer displays intense green-to-yellow fluorescence in both solution and the solid state. Remarkably, it shows acid-responsive color changes and a photoluminescence “turn-OFF” response upon protonation. The heteroaromatic macrocycle represents a versatile scaffold for the development of advanced optoelectronic materials and supramolecular host–guest systems.
“Synthesis of Solubility-Enhanced 6,8-Diarylated Dibromodibenzo[a,j]Phenazines via Pd-Catalyzed C─H Arylation and Skeletal Rearrangement"
Naohiro Namba, Norimitsu Tohnai, Satoshi Minakata*, and Youhei Takeda*
Asian J. Org. Chem. 2025, 14, e70211/1–5. DOI:10.1002/ajoc.70211
*Open-access article"!
*Invited as a part of a Honorary Collection on "In Memory of Professor Masahiko Iyoda"!
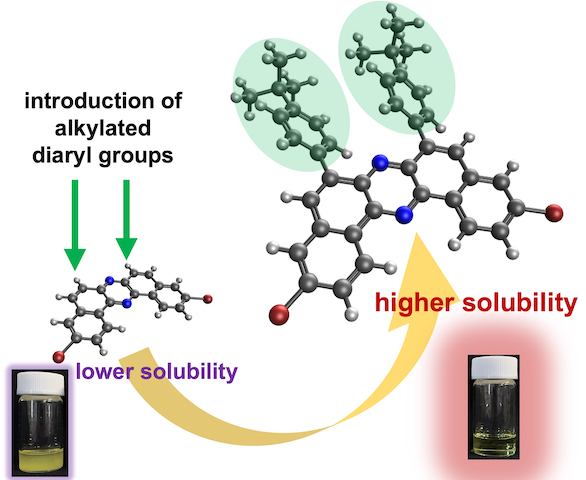
Abstract: We report the synthesis of a new class of dibromodibenzo[a,j]phenazine (DBPHZ) derivatives bearing diaryl substituents at the 6,8–positions. These compounds were obtained through a combination of regioselective Pd-catalyzed C─H direct arylation and oxidative skeletal rearrangement of appropriately functionalized binaphthalenediamines. The compatibility of bromine substituents with the C─H arylation conditions was confirmed, enabling the incorporation of various aryl groups including diphenyl, tert-butylphenyl, and 3,5-dimethylphenyl moieties. Crystallographic analysis of a representative compound revealed that the diaryl units adopt a twisted geometry relative to the DBPHZ core. Solubility tests demonstrated that the introduction of diaryl substituents having alkyl groups significantly enhances solubility in common organic solvents such as toluene and chloroform, compared to unsubstituted DBPHZ. Owing to the retained dibromo functionality, the synthesized DBPHZs would serve as valuable synthetic building blocks for constructing π-extended functional organic materials.
“Versatile method for the synthesis of aminobenziodoxolones and its application to one-pot coupling of arylboronic acids with simple amines"
Kazuki Kawanaka, Shunsuke Narita, Kensuke Kiyokawa*, and Satoshi Minakata*
Chem. Sci. 2025, 16, 19389–19396. DOI:10.1039/D5SC06301A
*Open-access article"!
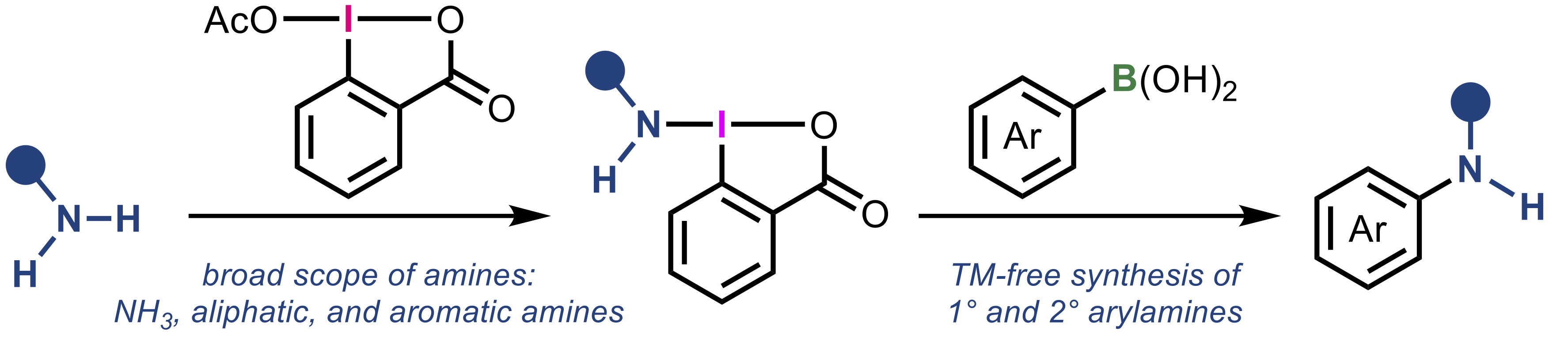
Abstract: Hypervalent iodine(III) compounds containing transferable nitrogen functional groups, amino-λ3-iodanes, were synthesized via a straightforward protocol utilizing simple amines and a benziodoxolone framework. This strategy enabled the use of a wide variety of amines, including ammonia, aliphatic and aromatic primary amines, significantly expanding the scope of accessible compounds compared to existing methods. The synthesized aminobenziodoxolones were applied to the oxidative amination of arylboronic acids, offering a practical transition-metal-free protocol for the synthesis of arylamines. To further demonstrate the synthetic utility, a one-pot process using in situ prepared aminobenziodoxolones was developed, allowing efficient coupling of boronic acids with various simple and pharmaceutically relevant amines. Furthermore, the method was extended to the synthesis of 15N-labelled arylamines, highlighting the versatility and practical value of this approach.
“Nitrogen-Centered Radical-Directed C(sp3)−H Amination and Aminoalkylation Using (Diarylmethylene)amino Benziodoxolones"
Kensuke Kiyokawa*, Mari Sugimura, Megumi Abe, Daiki Wada, Hikaru Kaneba, and Satoshi Minakata*
ChemistryEurope 2025, 3, e202500188. DOI:10.1002/ceur.202500188
*Open-access article"!
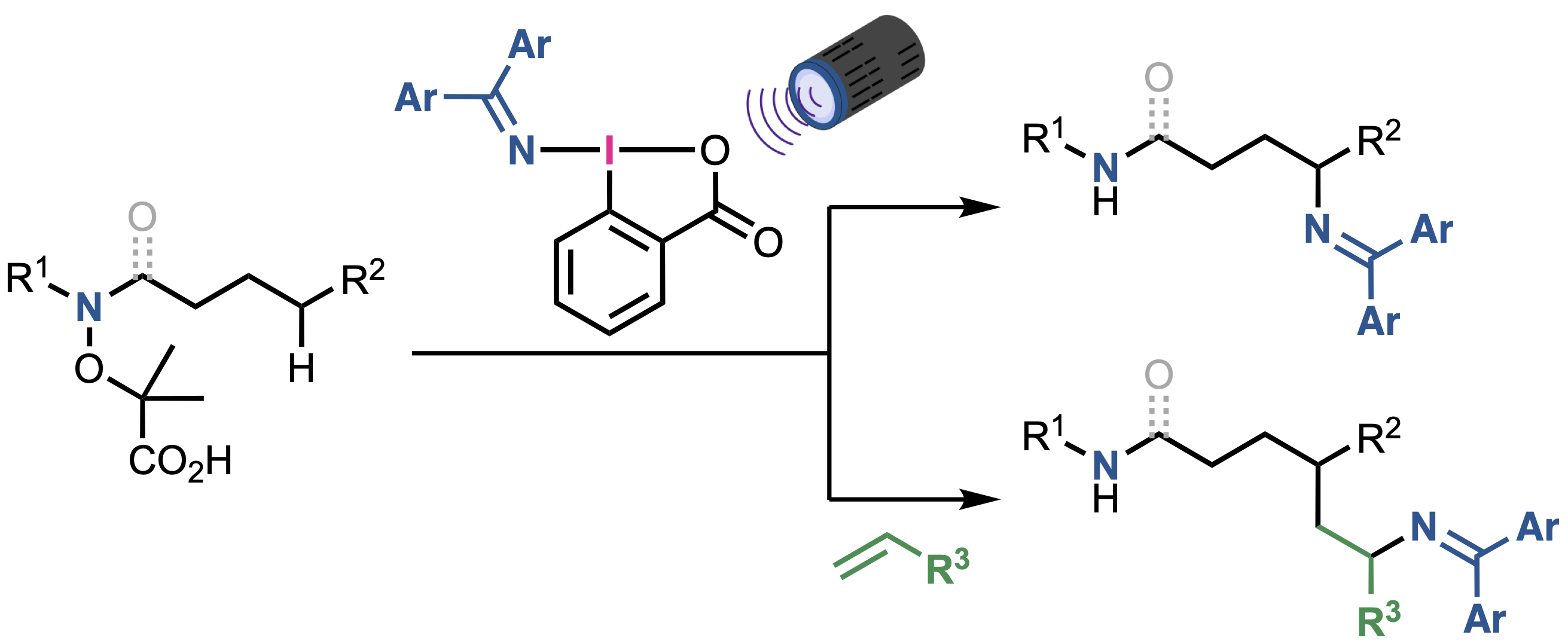
Abstract: Intermolecular C(sp3)−H functionalization via nitrogen-centered radical-directed 1,5-hydrogen atom transfer (HAT) is a powerful strategy for rapidly constructing functionalized molecules. Despite the obvious potential, applying this approach to aminofunctionalization remains challenging. Herein, a photochemical method is reported for C(sp3)−H aminofunctionalization that is achieved using hypervalent iodine-based aminating reagents—(diarylmethylene)amino benziodoxolones (DABXs). These reagents act as both single-electron oxidants and sources of nitrogen-based SOMOphiles (iminyl radicals), which enables the site-selective amination and aminoalkylation of α-aminoxy acid derivatives via 1,5-HAT. Notably, this reaction proceeds efficiently under mild reaction conditions without external photosensitizers to offer a practical and versatile method for the syntheses of readily modifiable diamines and aminoamides.
“Iodine-Catalyzed Stereospecific anti-Diamination of trans-β-Methylstyrene"
Takeshi Sugiyama, Chiyuki Naito, and Satoshi Minakata*
Org. Synth. 2025, 102, 203–216. DOI:10.15227/orgsyn.102.0203
*Open-access article"!
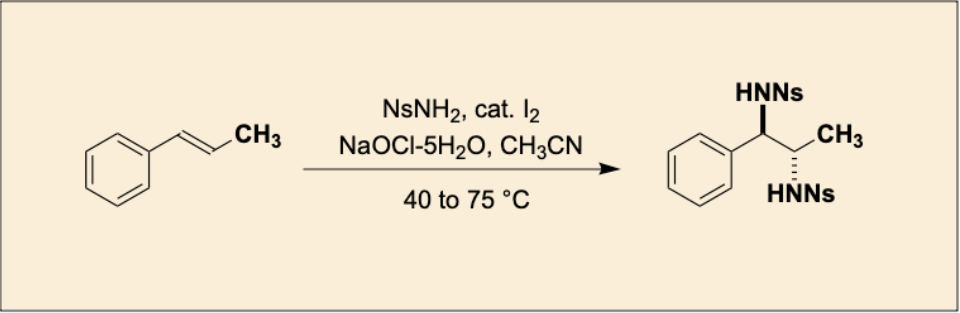
Abstract: In this study, we developed an environmentally friendly synthetic method that achieves the stereospecific anti-diamination of trans-β-methylstyrene with high selectivity and yield, utilizing an iodine catalyst and sodium hypochlorite pentahydrate.
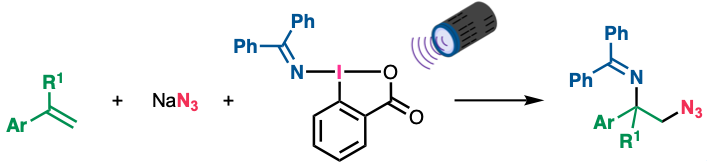
“Photoinduced Azidoamination of Styrenes Using Sodium Azide and (Diphenylmethylene)amino Benziodoxolone"
Kensuke Kiyokawa*, Koki Nakano, Daichi Okumura, and Satoshi Minakata*
Chem. Asian J. 2025, 20, e202401493/1–4. DOI:10.1002/asia.202401493