PROJECT
JST-CREST
Project:Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST), Core Research for Evolutional Science and Technology (CREST)
Research Area:
Establishment of innovative manufacturing technology based on nanoscience
Research Theme:
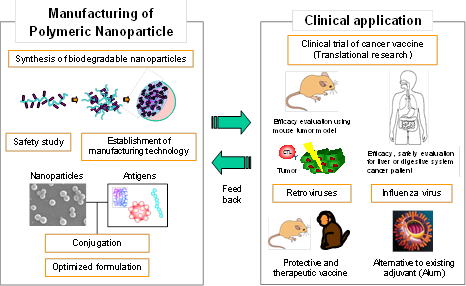
Manufacturing of Polymeric Nanoparticle Vaccines with Control Capability of Immune Responses
Principle investigator:
Mitsuru Akashi (Osaka University)
Collaborators:
Masanori Baba (Kagoshima University)
Tomohide Tatsumi (Osaka University)
Study Duration:
October 2007 ? March 2013 (5.5 years)
This project is aimed at the development of biodegradable polymer-based nanoparticles with control capability of immune responses, and the establishment of manufacturing technology and pharmaceutical process for practical applications of polymeric nanoparticle vaccines. We design and prepare a safe and universal nanoparticle-based vaccine using nanoparticles capable of controlling intracellular kinetic of antigens and having adjuvant activity. This strategy will provide a novel immune therapy for infectious diseases, cancers, and autoimmune diseases.
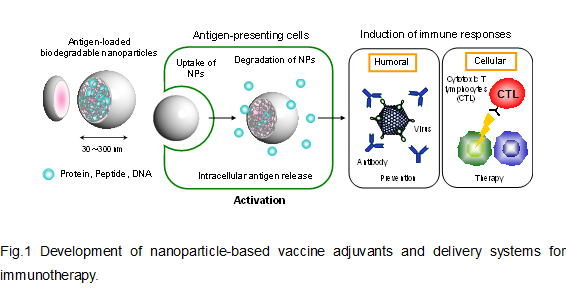
Induction of an adaptive immune response by vaccination is possible for a broad range of infectious diseases or cancers. Many of the vaccines currently in development are based on purified subunits, recombinant proteins, or synthetic peptides. However these new generation vaccines are less immunogenic than traditional vaccines and better delivery systems and adjuvants as an immune stimulator (immunostimulants) are required to induce acceptable immune responses. Polymeric nano/microparticles have been shown to possess significant potential as antigen delivery systems and immunostimulants. In particular, biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles with entrapped antigens, such as proteins, peptides or DNA represent an exciting approach to control the intracellular release of antigens and to optimize the desired immune response via selective targeting of the antigen to antigen-presenting cells (APCs) (Fig.1).
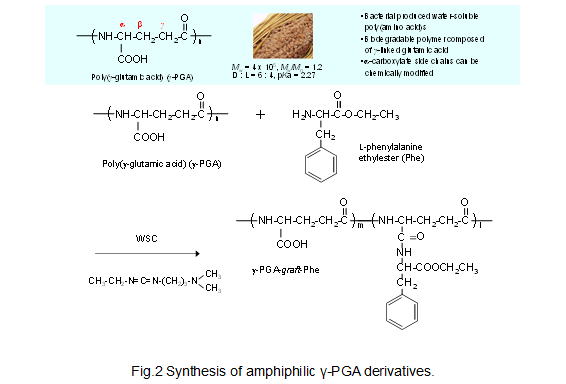
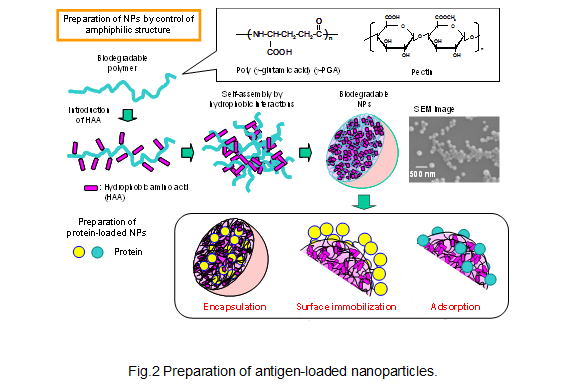
The efficient delivery of antigens to APCs, especially in dendritic cells (DCs) is one of the most important issues in the development of effective vaccines. In this project, we demonstrate the use of nanoparticles (NPs) composed of amphiphilic poly(amino acid) derivatives as vaccine delivery and adjuvants. We prepared antigen-loaded, biodegradable NPs composed of poly(γ-glutamic acid) (γ-PGA) conjugated with L-phenylalanine (Phe) as the hydrophobic segment (Fig.2 and 3). The NPs have significant potential as an antigen carrier and adjuvant for DCs. In addition, it has been demonstrated that antigen-encapsulated or -immobilized NPs are effective in vaccines against human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), influenza virus, Japanese encephalitis and cancers as compared to other adjuvant systems. This system provides a novel delivery tool and an efficient antigen delivery and adjuvant systems in the development of nanoparticle-based vaccines.
back to PROJECT